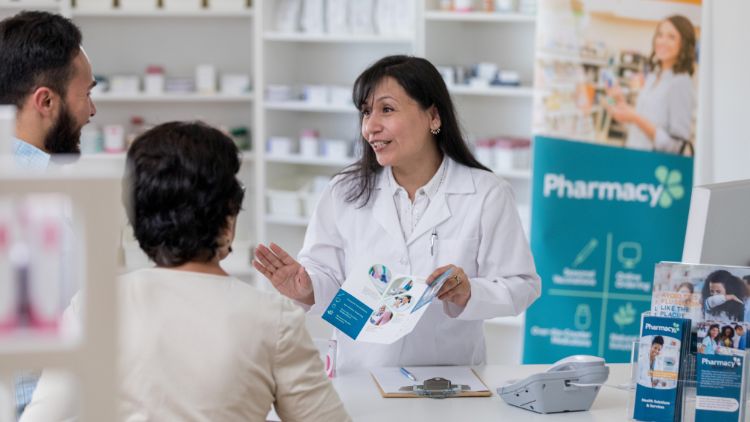
A pharmacist dispenses prescriptions and educates patients on how to utilize them safely. To become a pharmacist in Canada, you must first meet the requirements of your province or territory’s governing authority and then have practical job experience.
Pharmacist jobs in Canada are in high demand among people seeking employment in the healthcare field. The strong demand and competitive salary are two of the most attractive characteristics of this employment.
It is a stable and growing industry. Pharmacists are taking on new roles and responsibilities as the Canadian population ages and healthcare demands evolve.
This article will explain how to become a pharmacist in Canada, the skills needed, and answers some of the most often-asked questions about this profession.
How to Become a Pharmacist in Canada
Follow these five steps to become a pharmacist in Canada:
1. Enrol in a university and earn a degree
The first step toward becoming a pharmacist is to obtain a bachelor of science degree or a doctorate in pharmacy. A Bachelor of Science program lasts four years, but a Doctor of Pharmacy (PharmD) program lasts at least two years. You can attend any of the accredited universities, each with its admission standards.
2. Take the national board examination through the Pharmacy Examining Board of Canada (PEBC)
After graduating from your university pharmacy program, you can take the national board exam. The examination evaluates you in the following areas:
- patient care
- public health
- placement in practice
- health promotion
- communication and education
- quality and security
- Collaboration among and between professionals
- knowledge and research application
- ethical, legal, and professional requirements
The exam is divided into multiple-choice questions and an Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE). There are no requirements in Quebec.
3. Get practical experience
After passing the national board exam, you must undergo a practical training program. This training is frequently carried out under the supervision of a licensed pharmacist. A co-op, internship, or apprenticeship can provide this experience. Students use these programs to put their classroom knowledge to use.
4. Join a professional organization and get a license
Consider joining the Canadian Pharmacists Association. You can also apply to your province or territory’s regulatory authority to receive a license to practice pharmacy legally. For example, the College of Pharmacists of British Columbia is the province’s regulatory body for pharmacists. The standards for licensing vary by state.
5. Be fluent in English or French
Finally, learn how to communicate in English or French.
What Skills and Qualifications do Pharmacists Need?
Pharmacists must have hard and soft skills to accomplish their activities and obligations. They must also be physically fit and thoroughly understand clinical pharmacology. To be successful, pharmacists must have the following skills and certifications:
Teamwork skills
Pharmacists must work well with nurses, doctors, and other medical professionals. Teamwork skills include active listening and idea exchange.
Analytical and problem-solving skills
Pharmacists help customers take medications safely and must know how to assess their needs. You must also analyze the effects of multiple medications to keep customers safe.
Interpersonal and communication skills
You must be able to interact with others as a pharmacist. You must speak clearly with patients and obtain essential information from doctors.
Leadership skills
Pharmacists must be able to direct pharmacy technicians, clerks, and other professionals toward a common aim. They must be capable of encouraging and leading others.
Attention to detail
A pharmacist must follow prescriptions and provide consumers with safe medications. As a pharmacist, you must be detail-oriented and organized.
Computer proficiency
Pharmacists commonly use computer systems to access patient records, update prescription information, and confirm insurance details. You must understand how to use your pharmacy’s software system and enter data.
What is the Average Salary of a Pharmacist?
A pharmacist’s annual pay is $101,722 on average. Salaries vary depending on geography, expertise, and the needs of the recruiting healthcare facility.
Career & Job Prospects
Canada anticipates 12,500 new employment openings for pharmacy students by 2028. Pharma is an evergreen business and a highly demanding field because it always has something fresh to offer its practitioners.
A pharmacist’s average hourly wage in Canada is CAD 47.27, which is around INR 3600. An average pharmacist in the country earns CAD 91,956 per year, or INR 70 lakh. Here are the job prospects for different professions related to pharmacy –
- Pharmacy Manage (CAD 99,688)
- Pharmacist (CAD 92,625)
- Staff Pharmacist (CAD 90,821)
- Clinical Pharmacist (CAD 89,700)
- Pharmacy Technician (CAD 48,781)
- Technician (CAD 46,791)
Conclusion
Pharmacists in Canada can work full- or part-time at a drugstore chain, hospital, or independent pharmacy. Canadian pharmacist examinations are designed to help you advance your medical knowledge and find careers in management, business administration, and other disciplines.
Furthermore, the country offers an excellent environment for your growth and prosperity. To become a Pharmacist in Canada, you will need to study pharmacy courses in Canada to accomplish so. There are various famous universities in the country where students can pursue pharmaceutical degrees.




 Jobi.ng
Jobi.ng